Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time, is a critical economic indicator that affects the purchasing power of consumers, the cost of living, and the overall economic stability of a country. For India, one of the world's fastest-growing major economies, monitoring inflation and consumer prices is essential for policymakers, investors, and consumers alike. The Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED) from the St. Louis Fed provides comprehensive and up-to-date data on economic indicators, including inflation and consumer prices for India. This article delves into the insights provided by FRED on inflation and consumer prices in India, exploring trends, implications, and the significance of these economic metrics.
What is Inflation and Why is it Important?
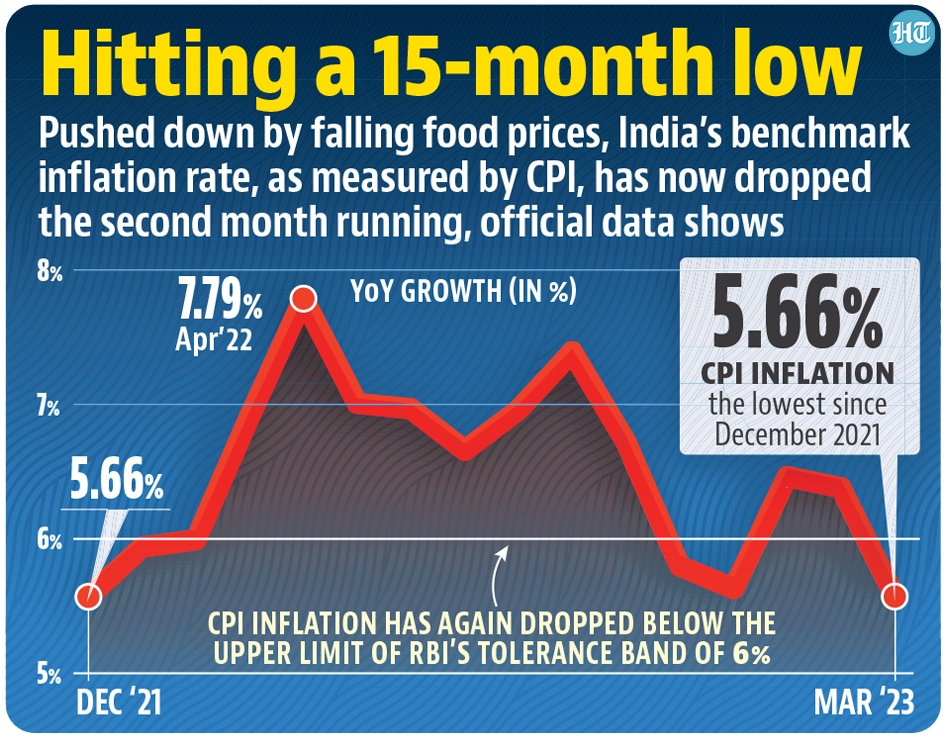
Inflation is measured as an annual percentage increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which is the most commonly used indicator of inflation. The CPI measures the average change in prices of a basket of goods and services consumed by households. In India, the CPI combines price data from urban and rural areas, providing a broad picture of price movements across the country. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of consumers, reduce the value of savings, and increase the cost of living, especially for low-income households. On the other hand, low and stable inflation supports economic growth by encouraging investment and consumption.
India's Inflation and Consumer Price Trends
According to data from FRED, India's inflation rate, as measured by the CPI, has fluctuated over the years, influenced by factors such as food prices, fuel prices, and monetary policy decisions. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the country's central bank, targets to keep inflation within a range of 2% to 6% to balance economic growth with price stability. Recent trends show that India has largely managed to keep its inflation rate within this target range, although there have been periods of deviation due to external and internal shocks.
Impact of Inflation on Consumers and the Economy
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/N7ENS4X5T5IF5LHEZB4N3BKKRU.jpg)
The impact of inflation on consumers in India is significant. High food inflation, in particular, affects a large portion of the population that spends a substantial portion of their income on food. The FRED data highlights the volatility in food prices, which can be influenced by factors such as weather conditions, agricultural production, and global commodity prices. For policymakers, managing inflation is crucial to ensure that economic growth is inclusive and sustainable. The RBI uses monetary policy tools, such as interest rates, to control inflation, while the government implements fiscal policies to support agriculture and control prices of essential commodities.
In conclusion, understanding inflation and consumer prices in India is vital for assessing the country's economic health and making informed decisions. The data from FRED provides valuable insights into India's inflation trends, highlighting the complexities and challenges of managing price stability in a large and diverse economy. As India continues to grow and integrate into the global economy, monitoring and managing inflation will remain a key priority for policymakers to ensure that the benefits of growth are shared by all. By leveraging data from reliable sources like FRED, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the economic landscape and contribute to policies and strategies that promote sustainable and inclusive growth.
For more information and the latest data on India's inflation and consumer prices, visit the FRED website.








/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/N7ENS4X5T5IF5LHEZB4N3BKKRU.jpg)